產品資訊
產品資訊
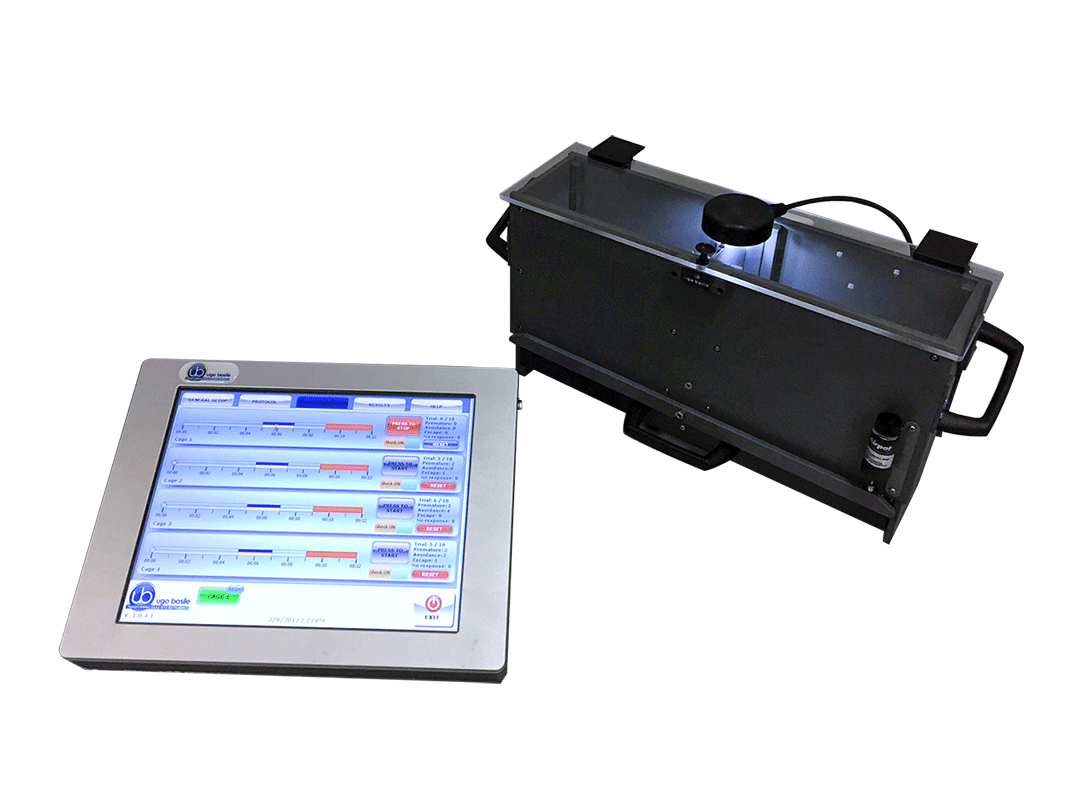
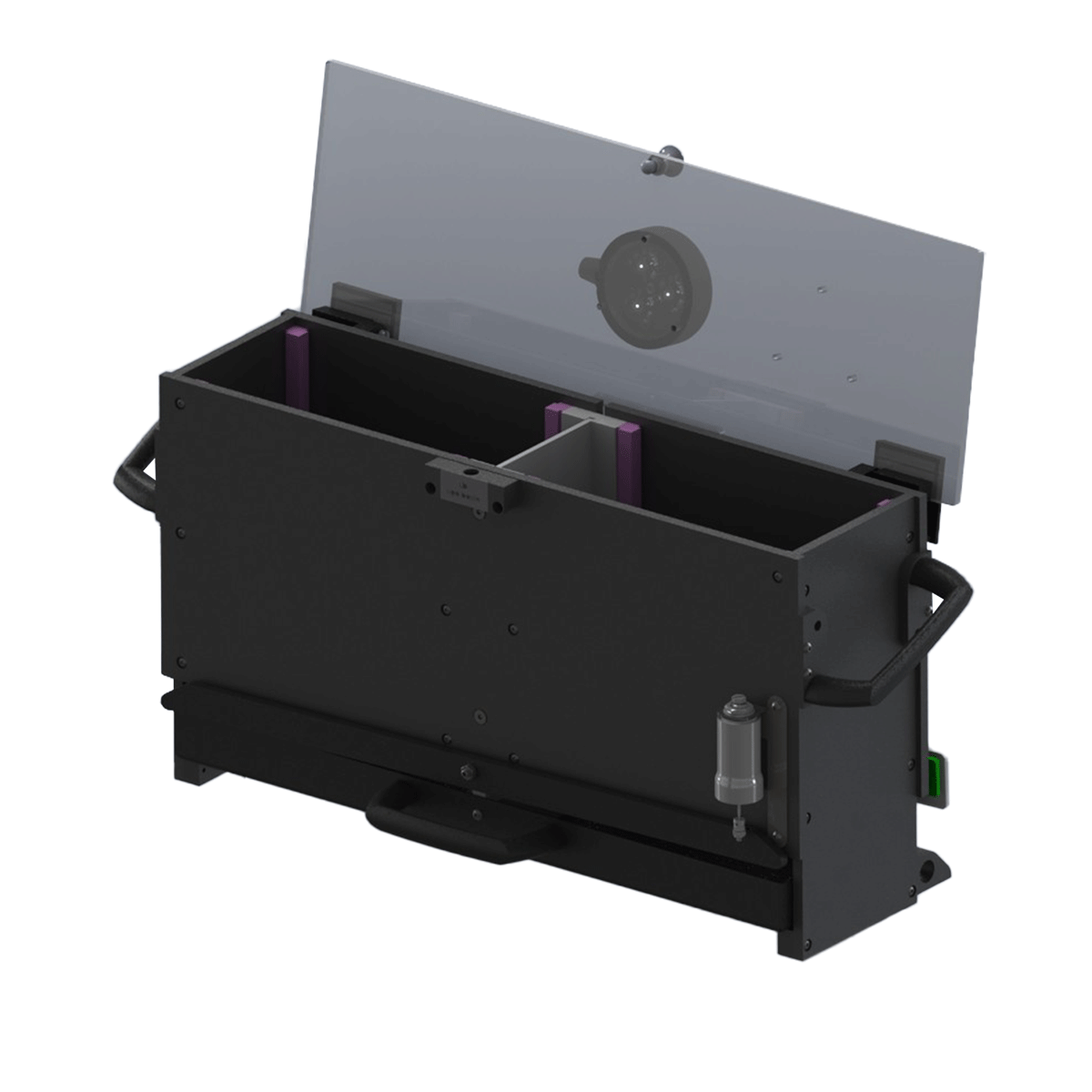
主動迴避測試儀 Automatic Reflex Conditioner (Active Avoidance)
產品型號: 40530
廠牌名稱: Ugo basile
主動迴避測試儀可完成所有經典的Pavlovian條件反射實驗。刺激方式可選擇聲音、光、電擊等,刺激的延遲時間、持續時間、暫停時間和強度可調。通過選配的印表機列印結果或通過軟體連接到電腦進行記錄分析。本實驗設備有分大鼠或小鼠配置。
產品特點
- 全套設備包含箱體及專用觸控平板系統,無需額外連接電腦
- 使用靜音閘門,開啟關閉皆不會造成噪音進而影響動物表現
- 獨家偵測技術,給您最準確的動物進出數據
- 各項實驗參數皆可自行設定,給您最有彈性的操作空間
主動迴避實驗是一種由恐懼驅使的迴避實驗,動物將透過電擊前的聲音提示學習得知即將到來的電擊,並前往安全室來避免掉電擊。
Ugo Basile 最新款的主動迴避測試儀在設計時即考量了各種迴避實驗的流程與步驟,外加使用者可以自行調整各項細節,因此可以做到各類型不同的迴避實驗。使用者只需要透過專用的觸控平板系統即可編輯/修改各項實驗參數。
測量結果包含了迴避次數、無回應次數、試驗間回應次數等。
A set up for testing active avoidance. By learning to predict the occurrence of an aversive event based on the presentation of a specific stimulus, the animal avoids the aversive event. Enables performance of a wide range of avoidance experiments using a flexible schedule. Precise detection of avoiding aversive event (moving to the other compartment). Manage up to 4 cages with one controller. Part of the Beehive cage-manager system.
Background
- Active avoidance is a fear-motivated associative avoidance task. By learning to predict the occurrence of an aversive event (shock) based on the presentation of a specific stimulus (tone), the animal avoids the aversive event by moving to a different compartment.
- Serves as an index of learning and allows memory to be assessed.
- Used in a wide range of studies including behavior genetics, psychopharmacology and behavioral toxicology. More recently these tests have been used in studies of aging, Alzheimer-type dementia and drug development.
Versatile, flexible schedule, precise detection
- Enables the researcher to perform a wide range of avoidance experiments, each according to a flexible schedule (using Timeline feature).
- Precise detection of animal crossing (moving to a different compartment). A tilting floor provides a simple, reliable detection mechanism for scoring animal movement across the two compartments. A partition with an intercommunicating opening at floor level divides the cage.
- The intuitive electronic unit display controls up to 4 cages, incorporates a constant-current high precision 8-pole shocker and manages data acquisition.
- Measures recorded include:
- Number of avoidances (the mouse crossing to the other compartment during the warning signal)
- Number of non-responses (the mouse failing to cross to the other compartment during the trial)
- Response latency (latency to avoid or escape)
- Number of intertrial responses (i.e. crossing the barrier within the intertrial interval),
- Data are stored inside the unit and can be downloaded for further processing or analysis in Excel, Access, etc.
- Engineered with high contrast, non-reflective materials that are optimal for video tracking.
- Anti-slip, naturally warm, maze surface texture is selected for best rodent comfort.
- System includes a Controller, and a Cage for either rat or mouse.
- Part of the expandable Ugo Basile Beehive conditioning-cage project. Using a single touch-screen controller, you manage all cages.
產品規格
| Touch Screen Controller | |
| LCD | 12” with resistive touch screen |
| CPU Module Port | 2 USB Port 2.0; 1 Ethernet port 10/100Mb;1 DVI port for external monitor |
| Peripheral Port | 4 output for Sound, Shock and light; 1 Power supply 12V-2A |
| Expansion Bus Connection | 2 RJ11 connectors |
| General | |
| Shock | Constant current |
| Shock Intensity | from 0 to 3mA, in 0.1mA steps |
| Shock Duration | in 0.1s |
| Visible Light | 0-100, in steps of 5% |
| Sound frequency | 100-18.000Hz, in steps of 100Hz |
| Operating Temperature | 10° to 40°C |
| Pollution Degree | ≤ 2 |
| Number of Cages | Up to 4 (with expansion boxes) |
| Physical | |
| Dimensions |
25(d)x33(w)x5.5(h)cm (40500-001) 57x27x30(h)cm, I.D. 48x20x22(h) (40532) 47x18x25(h)cm, I.D. 38x9x17(h)cm (40533) |
| Weight |
2.7Kg (40500-001) 5.3 (40532) 3.5 (40533) |
| Shipping Weight |
Rat Set-Up 13Kg Mouse Set-Up 12Kg |
| Packing Dimensions | 80x60x44cm (Control Unit & one cage) |
應用領域
Behavioral scientists are well acquainted with avoidance methods that have been used for several decades, originally by psychologists, who were interested in animal behavior.
These procedures were later exploited by neuroscientists, who specifically perform sys-tematic studies of the behavioral changes mainly produced by brain lesions, to define the functions of different C.N.S. sections.
Avoidance tests were soon extended to several other areas of research such as behavior genetics, psychopharmacology and behavioral toxicology. More recently, such use has become routine in animal model studies of aging and of Alzheimer-type dementia, including the search for new drugs of potential therapeutic value, consisting of attenuation of behavioral deficits.